NEMA Connectors - A Guide to NEMA Plug Types
After reading all the EV charging-related blogs online, you may have encountered this acronym more times than you'd like to.
And until now, you only know it as a type of plug used in many electronic devices, including your electric vehicle.
This blog will help you better understand what NEMA plugs are and how they work with EVs.
What are NEMA connectors?
NEMA connectors refer to the power plugs and receptacles used in North America and other countries that follow the standards set by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association.
Formed in 1926 from the merging of the Electric Power Club and the Associated Manufacturers of Electrical Supplies, NEMA set the industry standards for the convenience and safety of consumers.
Before NEMA stepped in to standardize the plug and receptacle configurations in the US, manufacturers used different configurations that prevented interchangeability between products.
Today, two and three-pronged connectors are commonly found in homes around the world.
A standard NEMA connector in the US has current ratings ranging from 15 amps to 60 amps and voltage ratings between 125 volts to 600 volts.
Different combinations of current and voltage ratings mean different configurations, dimensions, and pin positions.
NEMA standards classify plugs and receptacles according to amperage rating and voltage rating.
Types of NEMA connectors
There are two main types of NEMA connectors: straight-blade or non-locking and curved-blade or twist-locking.
As the name suggests, straight blades or non-locking connectors are designed to be pulled out of the receptacles easily, which, while convenient, can also mean the connection is unsecure.
These types of plugs have a neutral wire and a hot wire, with some having a third ground wire.
A non-locking connector is a common sight in residential settings, with most household appliances using either a two-pole plug without a ground pin, or a two-wire plug with a grounding pin to connect to power outlets.
Meanwhile, curved blades or twist-locking connectors have a locking mechanism, which makes a more reliable connection for industrial applications.
By rotating the plug, the rotated blades latch into place and prevent any accidental disconnection from the power supply.
A power cord that uses a locking connector has a neutral conductor, a hot conductor, and a ground conductor.
These are often used in industrial and commercial settings, where there's a need for protection against accidental disconnection from the power system.
NEMA plugs, power cords, and receptacles
NEMA Power cords are power cables that use NEMA plugs to connect to receptacles.
NEMA connectors can either be the plug or the receptacle, depending on the naming convention.
Non-locking plugs and receptacles can be further subdivided into 25 types from NEMA 1 - NEMA 24 and the Travel Trailer Connector or the NEMA TT-30.
NEMA 1, NEMA 5, NEMA 6, and NEMA 14 are the most common connectors that you will see.
NEMA 1
NEMA 1 connectors are two-prong plugs and receptacles without a ground pin.
These are rated at 125 V and are popular for household use, such as in smart appliances and other small electronic devices, because of their compact design and wide availability.
NEMA 1 plugs are also compatible with the newer NEMA 5 plugs, which make them the top choice for manufacturers.
Some of the most common NEMA 1 connectors include NEMA 1-15P, NEMA 1-20P, and NEMA 1-30P.

NEMA 5
NEMA 5 connectors are three-phase circuits with a neutral connection, a hot connection, and a wire grounding.
Rated at 125V, it's commonly used in IT equipment like routers, computers, and network switches.
NEMA 5-15P, the grounded version of NEMA 1-15P, is one of the most common connectors used in the US.
So, your NEMA 1-15P can fit in NEMA 5-15R grounded receptacles.

NEMA 14
NEMA 14 connectors are four-wire connectors with two hot wires, a neutral wire, and a ground pin.
These have amperage ratings ranging from 15 amps to 60 amps and voltage ratings of 125/250 volts.
NEMA 14-30 and NEMA 14-50 are the most common type of these plugs, used in non-locking settings such as in dryers and electric ranges.
Like the NEMA 6-50, NEMA 14-50 connectors are also used to charge electric vehicles.

NEMA TT-30
NEMA Travel Trailer, also known as the RV 30, is commonly used to transfer power from a power source to an RV.
It has the same orientation as the NEMA 5, which makes it compatible with both the NEMA 5-15R and 5-20R receptacles.
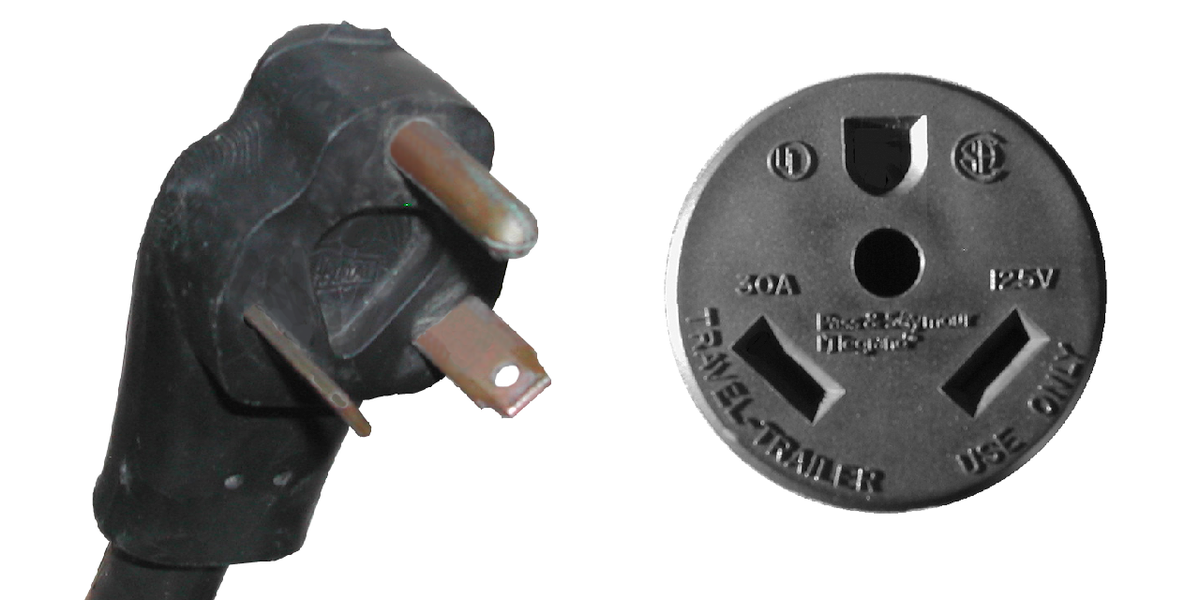

These are commonly found in RV parks as the standard for recreational vehicles.
Meanwhile, locking connectors have 24 subtypes, which include NEMA L1 up to NEMA L23 as well as the Midget Locking plugs or ML.
Some of the most common locking connectors are the NEMA L5, NEMA L6, NEMA L7, NEMA L14, NEMA L15, NEMA L21, and NEMA L22.
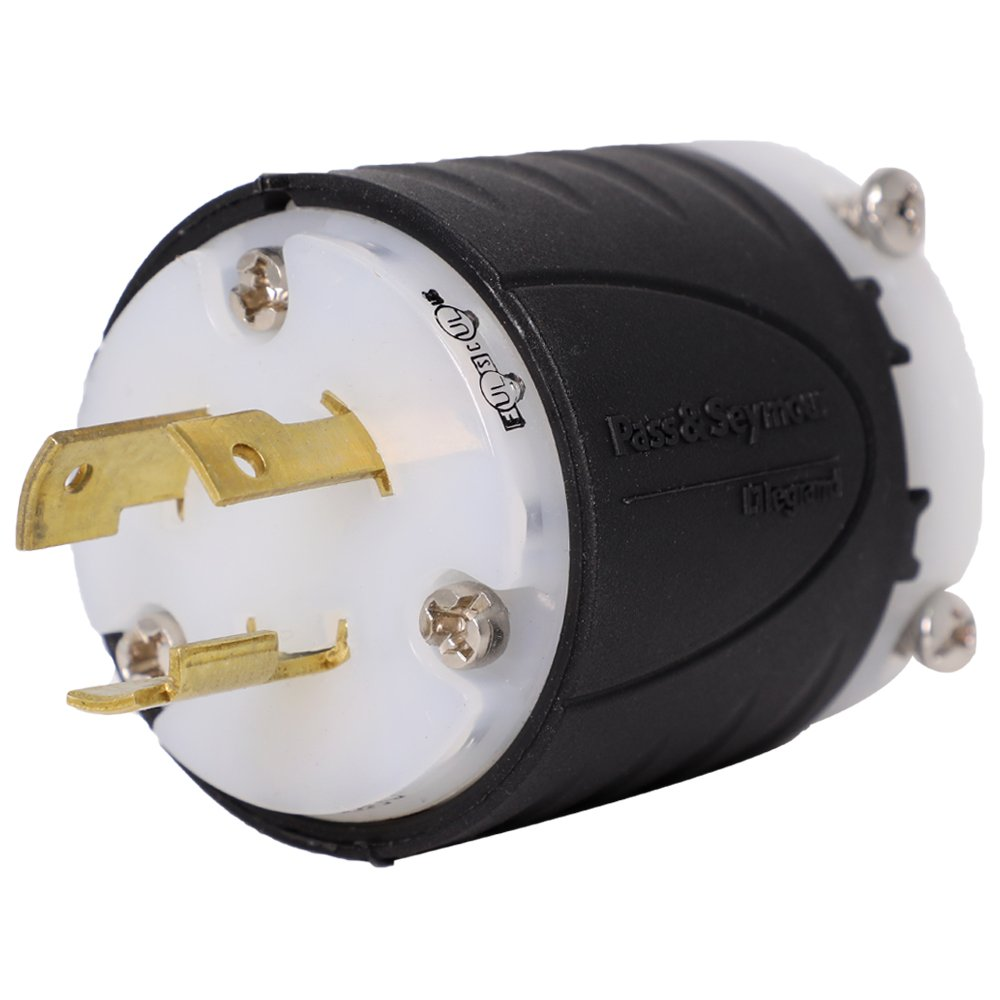
NEMA L5
NEMA L5 connectors are two-pole connectors with grounding.
These have a voltage rating of 125 volts, making them suitable for RV charging.
The NEMA L5-20 is commonly used for industrial settings where vibrations are likely to happen, such as in campsites and marinas.

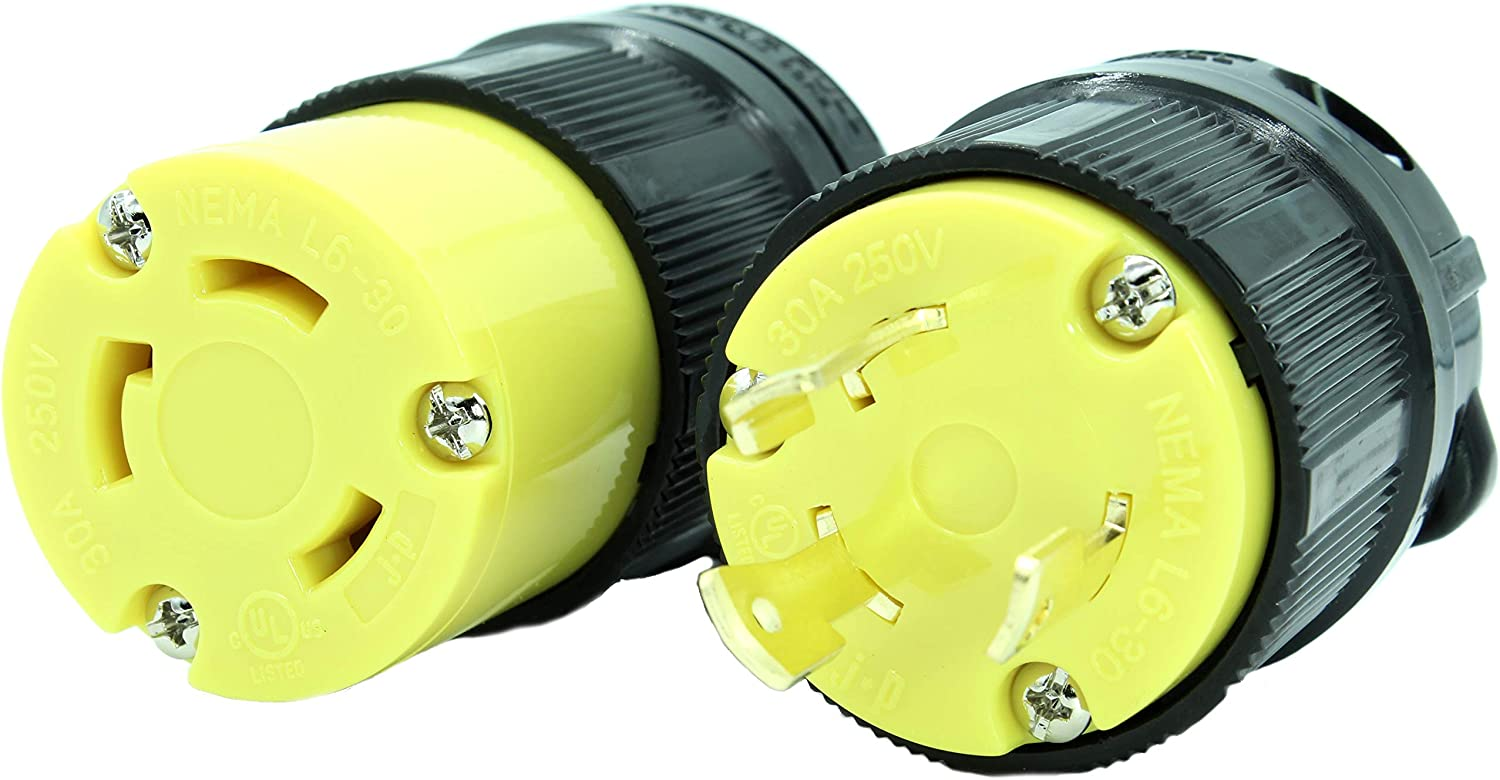
NEMA L6
NEMA L6 are two-pole, three-wire connectors without a neutral connection.
These connectors are rated at either 208 volts or 240 volts and are commonly used for generators (NEMA L6-30).

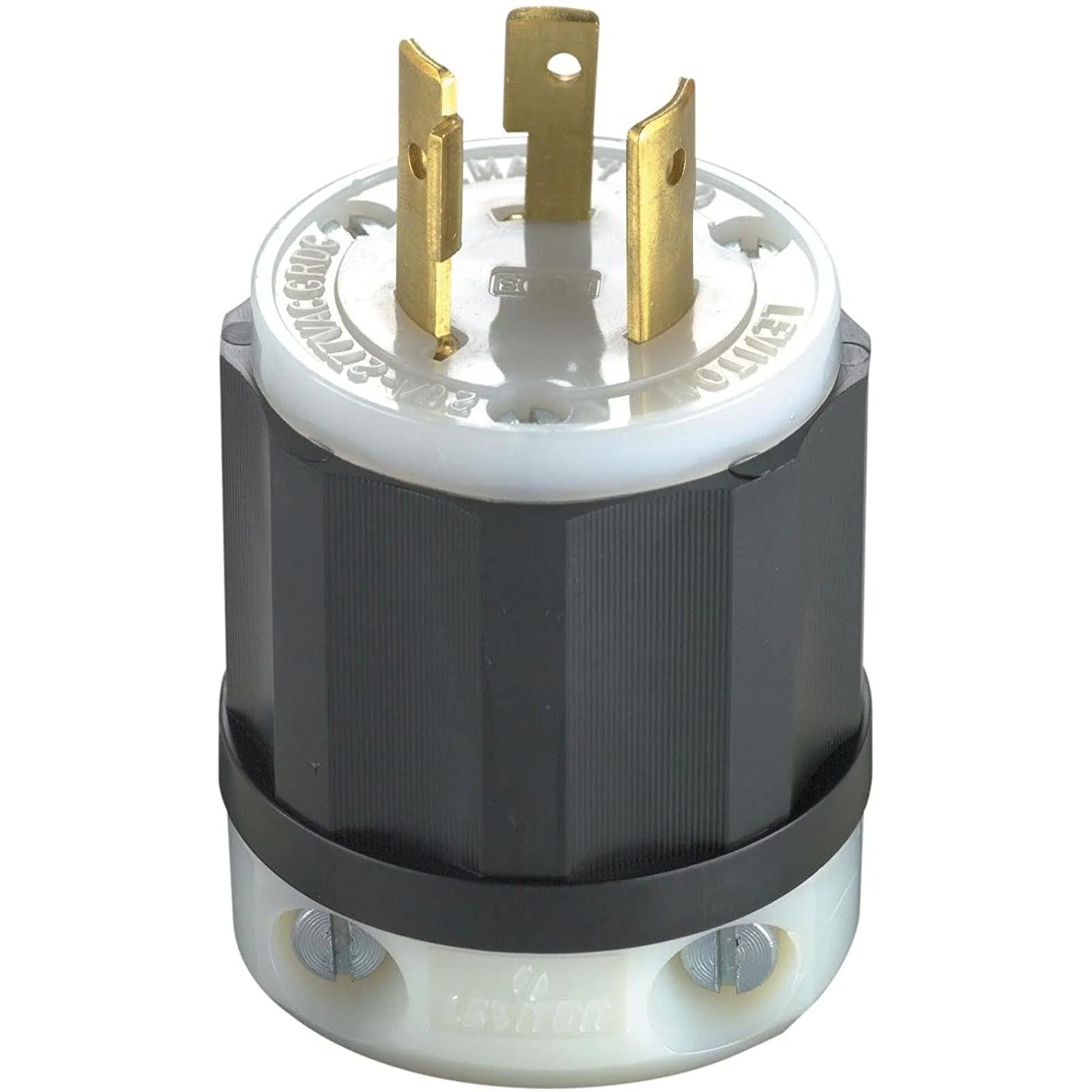
NEMA L7
NEMA L7 connectors are two-pole connectors with grounding and are commonly used for lighting systems (NEMA L7-20).

NEMA L14
NEMA L14 connectors are three-pole, grounded connectors with a voltage rating of 125/250 volts.
They're commonly used on large audio systems as well as on small generators.
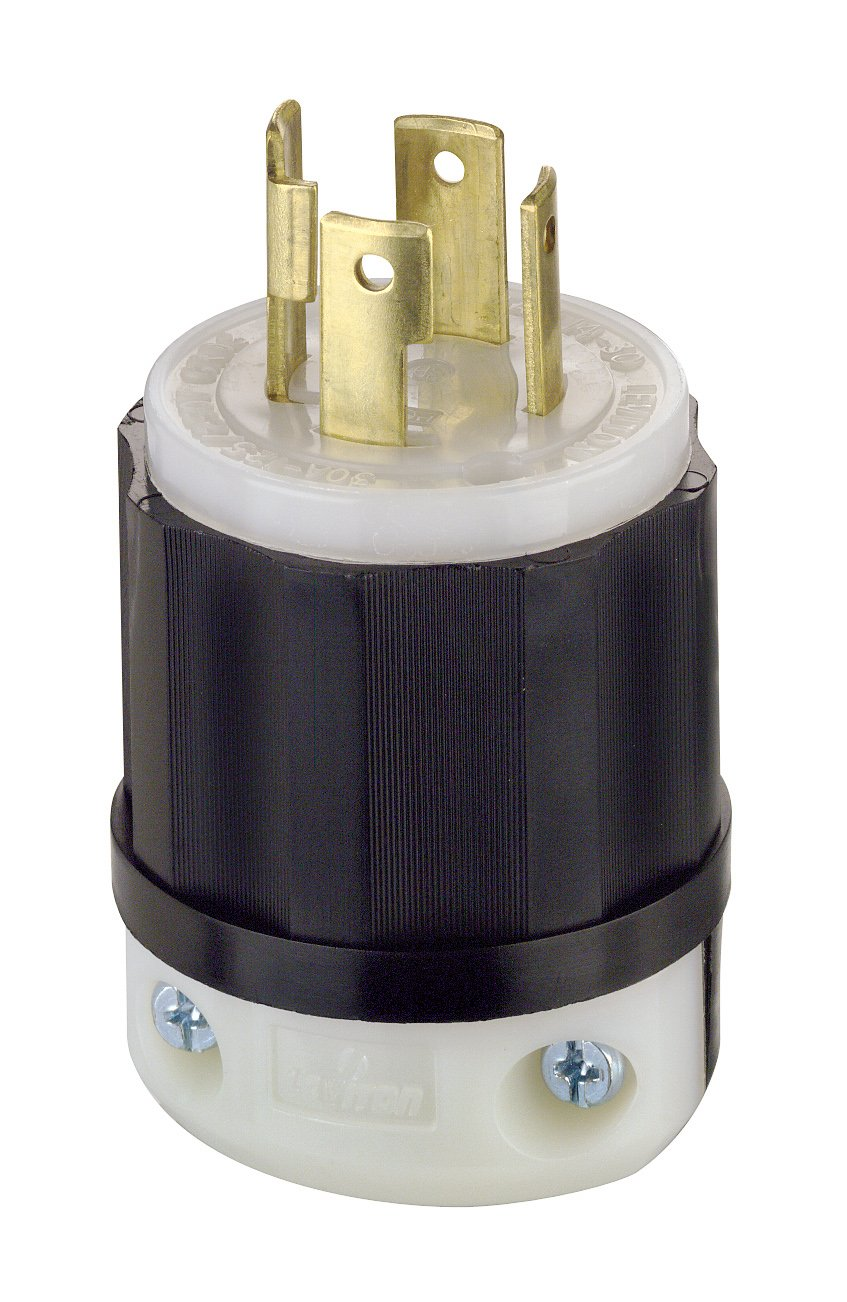

NEMA L-15
NEMA L-15 are four-pole connectors with a wire grounding.
These are weather-resistant receptacles that are commonly used for heavy-duty commercial applications.
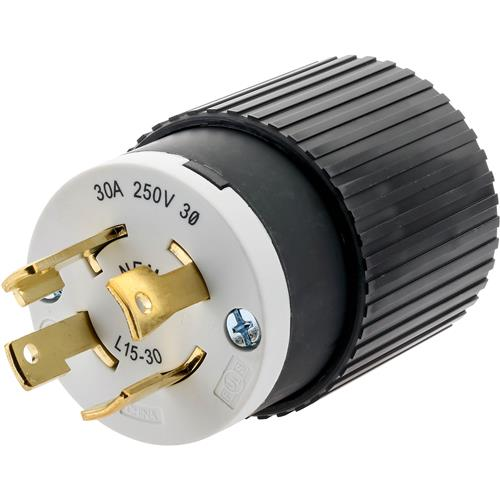

NEMA L21
NEMA L21 connectors are four-pole connectors with wire grounding rated at 120/208 volts.
These are tamper-resistant receptacles with a watertight seal that are suitable to use in damp environments.

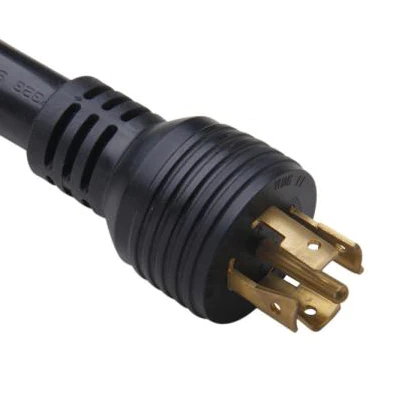
NEMA L22
NEMA L22 connectors have a four-pole configuration with wire grounding and a voltage rating of 277/480 volts.
These are often used on industrial machines and generator cords.

Understanding NEMA codes
The National Electrical Manufacturer's Association has devised a naming convention to standardize NEMA connectors.
The code has two parts: a number before the dash and a number after the dash.
The first number represents the plug configuration, which includes the voltage rating, the number of poles, and the number of wires. Ungrounded connectors have the same number of wires and poles because they don't require a grounding pin.
See the below chart for reference:
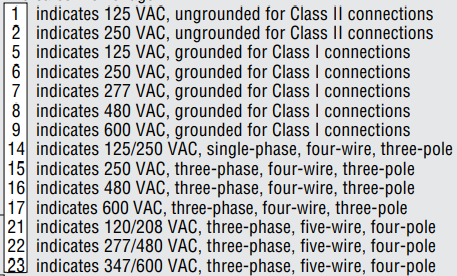
Meanwhile, the second number represents the current rating. The standard amperages are 15 amps, 20 amps, 30 amps, 50 amps, and 60 amps.
To put this into perspective, a NEMA 5-15 connector is a two-pole, two-wire connector with a voltage rating of 125 volts and a current rating of 15 amps.
For some connectors, the naming convention will have additional letters before the first number and/or after the second number.
The first letter, "L" is only found in locking connectors to indicate that it's indeed a locking type.
The second letter, which could be "P" or "R" indicates whether the connector is a "Plug" or a "Receptacle".
For example, a NEMA L5-30P is a locking plug with two poles, two wires, a current rating of 125 volts, and an amperage of 30 amps.
FAQs
What is a NEMA style outlet?
A NEMA style outlet refers to any receptacle used for AC or DC power transfer that follows the standards set by the National Electrical Manufacturers Association as well as the National Electrical Code.
What do NEMA plug numbers mean?
The first number represents the plug configuration, which includes the voltage rating, the number of poles, and the number of wires. Meanwhile, the second number represents the current rating which could be 15 amps, 20 amps, 30 amps, 50 amps, or 60 amps.
What is the difference between a NEMA and a non-NEMA connector?
The difference between a NEMA and a non-NEMA connector can be seen on the blades and the grounding pole on the plug. A NEMA plug's grounding pole has the same thickness as the other blades for more secure connections, whereas a non-NEMA plug's grounding stem is thinner and hollow inside.
Best Lectron Products for Multi-Network Charging
Trusted by 1M+ drivers; featured in


